Pinocchio examples

This is an example tutorial of how to setup pinocchio with pycapacity to calculate and visualise the robot capacities

Installing Pinocchio
Pinocchio library can be downloaded as sa pip package however due to the large number of different dependencies we suggest you to use anaconda.
Pip package install
Install the pinocchio library
pip install pin
Install an additional library with robot data example_robot_data provided by pinocchio community as well more info
pip install example-robot-data
Finally install the visualisation library meshcat that is compatible with pinocchio simple and powerful visualisaiton library more info
pip install meshcat
Finally install pycapacity for the workspace analysis
pip install pycapacity
Also you can install ipython of jupyter for simplicity.
Anaconda install
For anaconda instals you can simply download the yaml file and save it as env.yaml:
name: pio_examples
channels:
- defaults
- conda-forge
dependencies:
- python=3
- conda-forge::pinocchio
- conda-forge::gepetto-viewer
- conda-forge::gepetto-viewer-corba
- conda-forge::example-robot-data
- conda-forge::meshcat-python
- pip
- pip:
- pycapacity
And create a new ready to go environment:
conda env create -f env.yaml # create the new environemnt and install pinocchio, gepetto, pycapacity,..
conda actvavte pio_examples
Creating the custom environment from scratch
You can also simply use anaconda to create a new custom environment:
conda create -n pio_examples python=3.8 pip # create python 3.8 based environment
conda activate pio_examples
Install all the needed packages
conda install -c conda-forge pinocchio
conda install -c conda-forge example-robot-data
conda install -c conda-forge gepetto-viewer
Then install pycapacity for the workspace analysis
pip install pycapacity
📢 NEW Examples!
- For some more examples check out the
examplesfolder of the repository. Interactive jupyter notebooks are available in the
examples/notebooksfolder: see on Github velocity polytope and reachable space polytopePython scripts are available in the
examples/scriptsfolder: see on Github
Code example
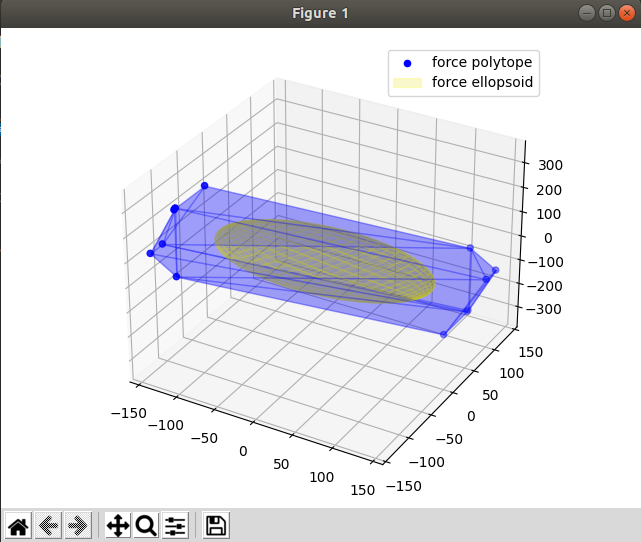
Calculating the force polytope and ellipsoid of the panda robot and visualising it using matplotlib.
import pinocchio as pin
import numpy as np
from example_robot_data import load
robot = load('panda')
# Display a robot configuration.
# q0 = pin.neutral(robot.model)
q0 = robot.q0
# calculate the jacobian
data = robot.model.createData()
pin.framesForwardKinematics(robot.model,data,q0)
pin.computeJointJacobians(robot.model,data, q0)
J = pin.getFrameJacobian(robot.model, data, robot.model.getFrameId(robot.model.frames[-1].name), pin.LOCAL_WORLD_ALIGNED)
# use only position jacobian
J = J[:3,:]
# polytope python module
import pycapacity.robot as pycap
# get max torque
t_max = robot.model.effortLimit
t_min = -t_max
# calculate force polytope
f_poly = pycap.force_polytope(J, t_max, t_min)
# calculate force ellipsoid
f_ellipsoid = pycap.force_ellipsoid(J, t_max)
# plotting the polytope
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pycapacity.visual import * # pycapacity visualisation tools
fig = plt.figure()
# draw faces and vertices
plot_polytope(plot=plt, polytope=f_poly, label='force polytope', vertex_color='blue', face_color='blue', edge_color='blue', alpha=0.2)
# draw the ellipsoid
plot_ellipsoid(ellipsoid=f_ellipsoid,plot=plt,color='yellow', edge_color='yellow', alpha=0.2, label="force ellipsoid")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
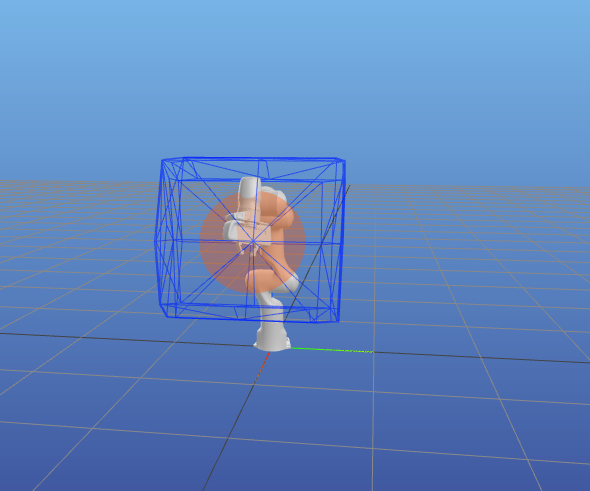
Visualise polytopes in Meshcat
Calculating the velocity polytope and ellipsoid of the panda robot and visualising it using meshcat.
import pinocchio as pin
import numpy as np
import time
from example_robot_data import load
# import pycapacity
import pycapacity as pycap
# get panda robot usinf example_robot_data
robot = load('panda')
# get joint position ranges
q_max = robot.model.upperPositionLimit.T
q_min = robot.model.lowerPositionLimit.T
# get max velocity
dq_max = robot.model.velocityLimit
dq_min = -dq_max
# Use robot configuration.
# q0 = np.random.uniform(q_min,q_max)
q0 = (q_min+q_max)/2
# calculate the jacobian
data = robot.model.createData()
pin.framesForwardKinematics(robot.model,data,q0)
pin.computeJointJacobians(robot.model,data, q0)
J = pin.getFrameJacobian(robot.model, data, robot.model.getFrameId(robot.model.frames[-1].name), pin.LOCAL_WORLD_ALIGNED)
# use only position jacobian
J = J[:3,:]
# end-effector pose
Xee = data.oMf[robot.model.getFrameId(robot.model.frames[-1].name)]
## visualise the robot
from pinocchio.visualize import MeshcatVisualizer
viz = MeshcatVisualizer(robot.model, robot.collision_model, robot.visual_model)
# Start a new MeshCat server and client.
viz.initViewer(open=True)
# Load the robot in the viewer.
viz.loadViewerModel()
viz.display(q0)
# small time window for loading the model
# if meshcat does not visualise the robot properly, augment the time
# it can be removed in most cases
time.sleep(0.2)
## visualise the polytope and the ellipsoid
import meshcat.geometry as g
# calculate the polytope
opt = {'calculate_faces':True}
# calculate the polytope
vel_poly = pycap.robot.velocity_polytope(J, dq_min, dq_max,options=opt)
# meshcat triangulated mesh
poly = g.TriangularMeshGeometry(vertices=vel_poly.vertices.T/10 + Xee.translation, faces=vel_poly.face_indices)
viz.viewer['poly'].set_object(poly, g.MeshBasicMaterial(color=0x0022ff, wireframe=True, linewidth=3, opacity=0.2))
# calculate the ellipsoid
vel_ellipsoid = pycap.robot.velocity_ellipsoid(J, dq_max)
# meshcat ellipsoid
ellipsoid = g.Ellipsoid(radii=vel_ellipsoid.radii/10)
viz.viewer['ellipse'].set_object(ellipsoid, g.MeshBasicMaterial(color=0xff5500, transparent=True, opacity=0.2))
viz.viewer['ellipse'].set_transform(pin.SE3(vel_ellipsoid.rotation, Xee.translation).homogeneous)
Animate polytopes in Meshcat
Calculating the velocity polytope and ellipsoid of the panda robot and visualising it using meshcat.
import pinocchio as pin
import numpy as np
from example_robot_data import load
# get panda robot usinf example_robot_data
robot = load('panda')
# get joint position ranges
q_max = robot.model.upperPositionLimit.T
q_min = robot.model.lowerPositionLimit.T
# get max velocity
dq_max = robot.model.velocityLimit
dq_min = -dq_max
# Use robot configuration.
q = (q_min+q_max)/2
## visualise the robot
from pinocchio.visualize import MeshcatVisualizer
viz = MeshcatVisualizer(robot.model, robot.collision_model, robot.visual_model)
# Start a new MeshCat server and client.
viz.initViewer(open=True)
# Load the robot in the viewer.
viz.loadViewerModel()
viz.display(q)
import pycapacity as pycap
import meshcat.geometry as g
while True:
# some sinusoidal motion
for i in np.sin(np.linspace(-np.pi,np.pi,200)):
# update the joint position
q[0] = i
q[1] = i
q[2] = i
# calculate the jacobian
data = robot.model.createData()
pin.framesForwardKinematics(robot.model,data,q)
pin.computeJointJacobians(robot.model,data, q)
J = pin.getFrameJacobian(robot.model, data, robot.model.getFrameId(robot.model.frames[-1].name), pin.LOCAL_WORLD_ALIGNED)
# use only position jacobian
J = J[:3,:]
# end-effector pose
Xee = data.oMf[robot.model.getFrameId(robot.model.frames[-1].name)]
# calculate the polytope
opt = {'calculate_faces':True}
# calculate the polytope
vel_poly = pycap.robot.velocity_polytope(J, dq_min, dq_max,options=opt)
# visualise the robot
viz.display(q)
# visualise the polytope and the ellipsoid
# meshcat triangulated mesh
poly = g.TriangularMeshGeometry(vertices=vel_poly.vertices.T/10 + Xee.translation, faces=vel_poly.face_indices)
viz.viewer['poly'].set_object(poly, g.MeshBasicMaterial(color=0x0022ff, wireframe=True, linewidth=3, opacity=0.2))
# calculate the ellipsoid
vel_ellipsoid = pycap.robot.velocity_ellipsoid(J, dq_max)
# meshcat ellipsoid
ellipsoid = g.Ellipsoid(radii=vel_ellipsoid.radii/10)
viz.viewer['ellipse'].set_object(ellipsoid, g.MeshBasicMaterial(color=0xff5500, transparent=True, opacity=0.2))
viz.viewer['ellipse'].set_transform(pin.SE3(vel_ellipsoid.rotation, Xee.translation).homogeneous)

📢 NEW Examples!
- For some more examples check out the
examplesfolder of the repository. Interactive jupyter notebooks are available in the
examples/notebooksfolder: see on Github velocity polytope and reachable space polytopePython scripts are available in the
examples/scriptsfolder: see on Github