Four link planar robot examples
Four link planar robot is one very common simplified robot model for different analysis and algorithm development.
It is composed of 4 links and 4 joints.
In order to facilitate testing with this simple robot model it is implemented within pycapacity package, inside the module examples withing the class FourLinkRobot, see the module for more info
📢 NEW Examples!
- For some more examples check out the
examplesfolder of the repository. Interactive jupyter notebooks are available in the
examples/notebooksfolder: see on GithubPython scripts are available in the
examples/scriptsfolder: see on Github
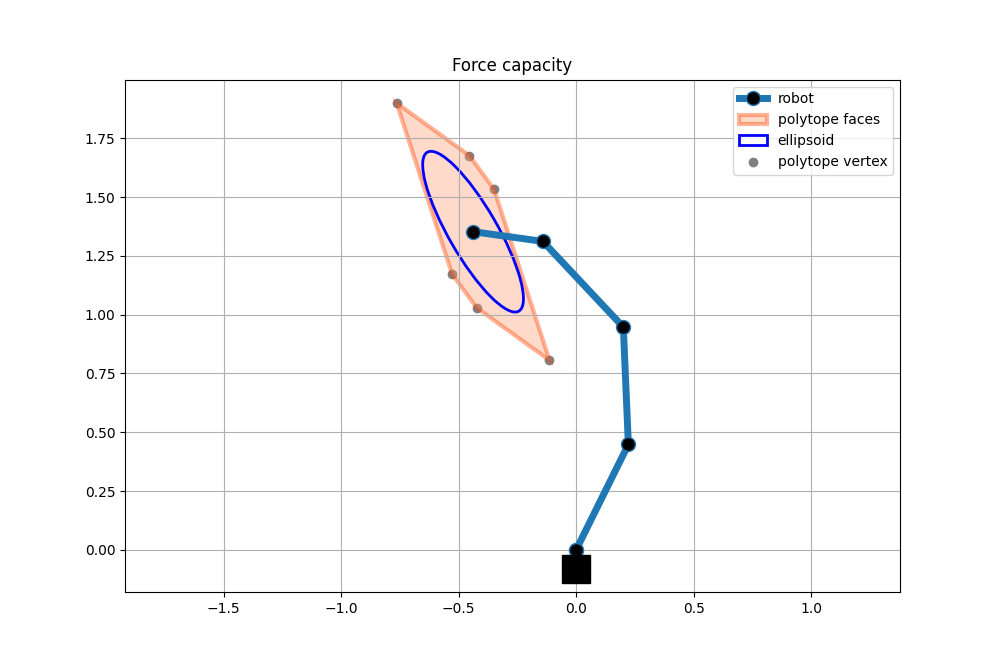
Force capacity polytope
Force polytope and ellipsoid for 4dof planar robot with random joint angles. The robot, polytope and ellipsoid are visualised using matplotlib.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pycapacity.robot import * # robot capacity module
from pycapacity.visual import * # visualistion tools
# four link robot import
from pycapacity.examples import FourLinkRobot
# create the robot
robot = FourLinkRobot()
# this seed is used to generate the same image
# as in the examples in the docs
np.random.seed(12345)
# joint positions q
q = np.random.rand(4)*np.pi/2-1
# joint torque limits tau
tau_min = -np.ones((4,1))
tau_max = np.ones((4,1))
# jacobian
J = robot.jacobian(q)
# calculate the force polytope
f_poly = force_polytope(J,tau_min,tau_max)
# calculate the force ellipsoid
f_ellipsoid = force_ellipsoid(J, tau_max)
# visualise polytope ellipsoid
fig = plt.figure(12, figsize=[10,10])
scale = 1/5
# plot the robot
robot_position = robot.forward_kinematics(q)
robot.plot(plt, q)
# plot the polytope
plot_polytope(plot=plt,
polytope=f_poly,
center=robot_position,
face_color='lightsalmon',
edge_color='orangered',
vertex_color='gray',
label='polytope',
scale=scale)
# plot ellipsoid
plot_ellipsoid(ellipsoid=f_ellipsoid,
center=robot_position,
plot=plt,
label='ellipsoid',
edge_color='blue',
alpha=1.0,
scale=scale)
plt.title('Force capacity')
plt.grid()
plt.axis('equal')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
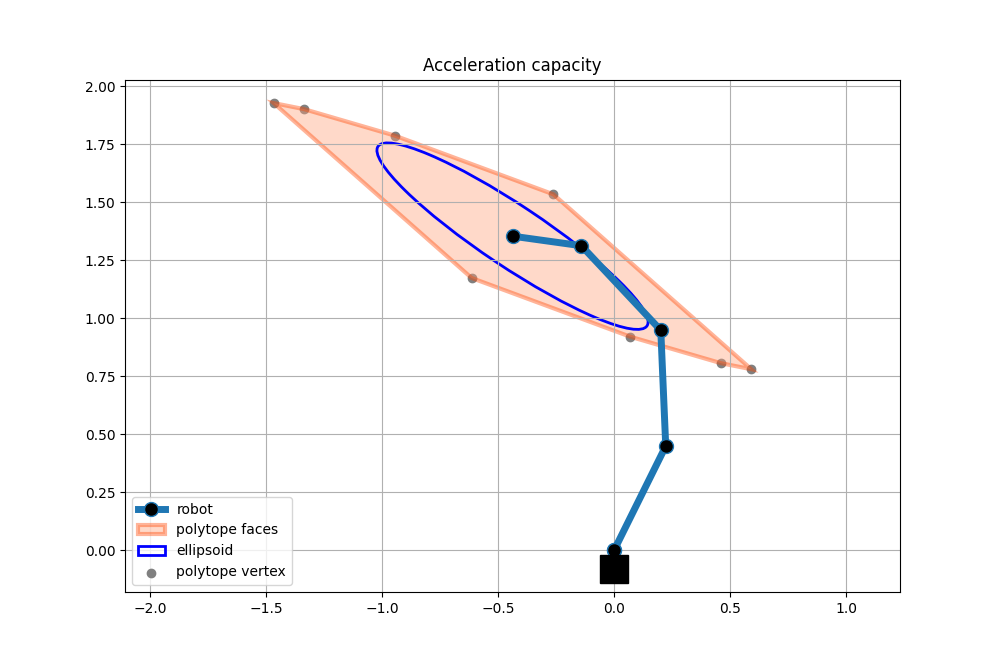
Acceleration capacity polytope
Acceleration polytope and ellipsoid for 4dof planar robot with random joint angles. The robot, polytope and ellipsoid are visualised using matplotlib.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pycapacity.robot import * # robot capacity module
from pycapacity.visual import * # visualistion tools
# four link robot import
from pycapacity.examples import FourLinkRobot
# create the robot
robot = FourLinkRobot()
# this seed is used to generate the same image
# as in the examples in the docs
np.random.seed(12345)
# joint positions q
q = np.random.rand(4)*np.pi/2-1
# joint torque limits tau
tau_min = -np.ones((4,1))
tau_max = np.ones((4,1))
# jacobian
J = robot.jacobian(q)
# jacobian
M = robot.inertia(q)
# calculate the velocity polytope
a_poly = acceleration_polytope(J, M, tau_min ,tau_max)
# calculate the velocity ellipsoid
a_ellipsoid = acceleration_ellipsoid(J, M, tau_max)
# visualise polytope ellipsoid
fig = plt.figure(13, figsize=[10,10])
scale = 1/50
# plot the robot
robot_position = robot.forward_kinematics(q)
robot.plot(plt, q)
# plot the polytope
plot_polytope(plot=plt,
polytope=a_poly,
center=robot_position,
face_color='lightsalmon',
edge_color='orangered',
vertex_color='gray',
label='polytope',
scale=scale)
# plot ellipsoid
plot_ellipsoid(ellipsoid=a_ellipsoid,
center=robot_position,
plot=plt,
label='ellipsoid',
edge_color='blue',
alpha=1.0,
scale=scale)
plt.title("Acceleration capacity")
plt.grid()
plt.axis('equal')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
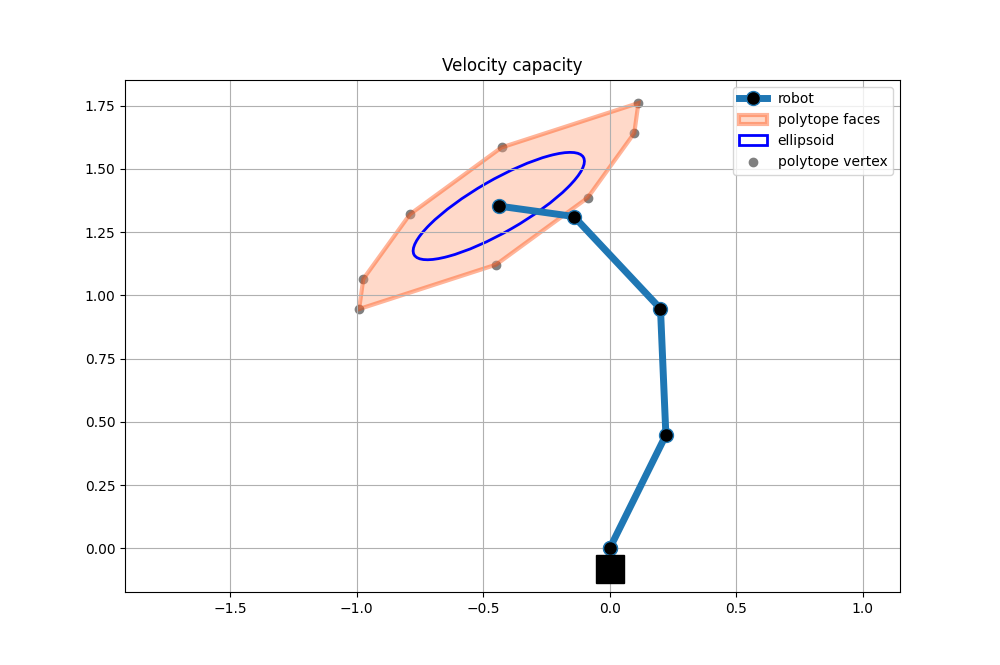
Velocity capacity polytope
Velocity polytope and ellipsoid for 4dof planar robot with random joint angles. The robot, polytope and ellipsoid are visualised using matplotlib.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pycapacity.robot import * # robot capacity module
from pycapacity.visual import * # visualistion tools
# four link robot import
from pycapacity.examples import FourLinkRobot
# create the robot
robot = FourLinkRobot()
# this seed is used to generate the same image
# as in the examples in the docs
np.random.seed(12345)
# joint positions q
q = np.random.rand(4)*np.pi/2-1
# joint torque limits tau
dq_min = -np.ones((4,1))
dq_max = np.ones((4,1))
# jacobian
J = robot.jacobian(q)
# calculate the velocity polytope
v_poly = velocity_polytope(J, dq_min ,dq_max)
# calculate the velocity ellipsoid
v_ellipsoid = velocity_ellipsoid(J, dq_max)
# visualise polytope ellipsoid
fig = plt.figure(14, figsize=[10,10])
scale = 1/5
# plot the robot
robot_position = robot.forward_kinematics(q)
robot.plot(plt, q)
# plot the polytope
plot_polytope(plot=plt,
polytope=v_poly,
center=robot_position,
face_color='lightsalmon',
edge_color='orangered',
vertex_color='gray',
label='polytope',
scale=scale)
# plot ellipsoid
plot_ellipsoid(ellipsoid=v_ellipsoid,
center=robot_position,
plot=plt,
label='ellipsoid',
edge_color='blue',
alpha=1.0,
scale=scale)
plt.title("Velocity capacity")
plt.grid()
plt.axis('equal')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
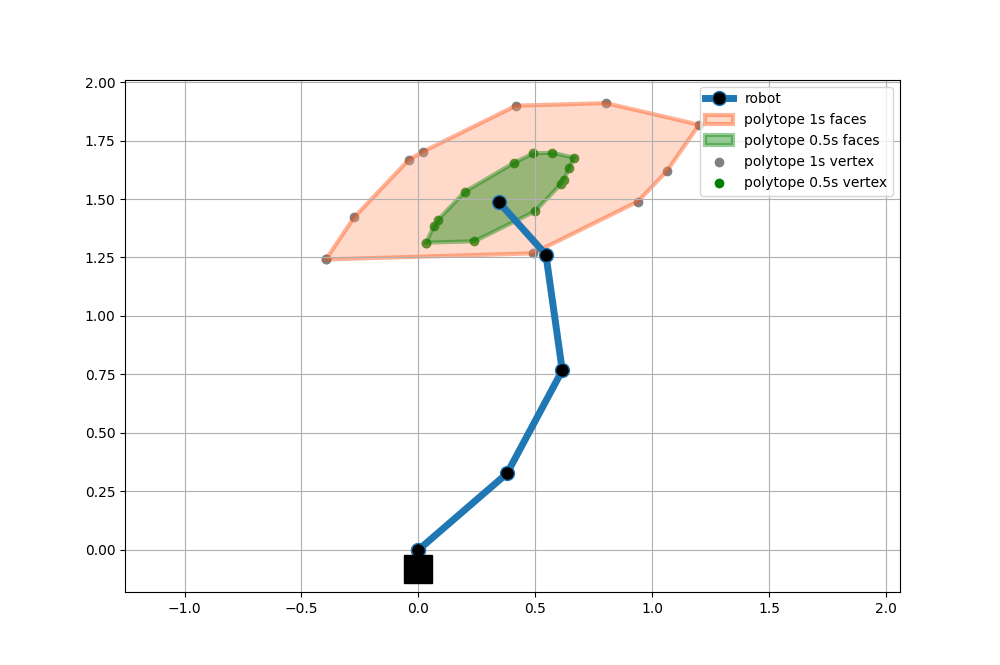
Reachable space polytope approximation
Reachable space polytope approximation for 4dof planar robot with random joint angles. The reachable space is calculated for two horizon times 1s and 0.5s.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pycapacity.robot import * # robot capacity module
from pycapacity.visual import * # visualistion tools
# four link robot import
from pycapacity.examples import FourLinkRobot
# create the robot
robot = FourLinkRobot()
# this seed is used to generate the same image
# as in the examples in the docs
np.random.seed(12345)
# joint torque limits tau
tau_min = -np.ones(4)*1
tau_max = np.ones(4)*1
# joint velocity limits
dq_min = -np.ones(4)
dq_max = np.ones(4)
# joint limits
q_min = -np.ones(4)
q_max = np.ones(4)
# random joint configuration
q = np.random.uniform(q_min, q_max)
# jacobian
J = robot.jacobian(q)
# jacobian
M = robot.inertia(q)
# calculate the reachable space polytope with 1s horizon
poly_dt1000 = reachable_space_approximation(J=J,
M=M,
q0=q,
horizon=1,
t_max=tau_max,
t_min=tau_min,
dq_max=dq_max,
dq_min=dq_min,
q_min = q_min,
q_max = q_max)
# calculate the reachable space polytope with 0.5s horizon
poly_dt500 = reachable_space_approximation(J=J,
M=M,
q0=q,
horizon=0.5,
t_max=tau_max,
t_min=tau_min,
dq_max=dq_max,
dq_min=dq_min,
q_min = q_min,
q_max = q_max)
# visualise polytope ellipsoid
fig = plt.figure(12, figsize=[10,10])
#plot the robot
robot_position = robot.forward_kinematics(q)
robot.plot(plt, q)
#plot the polytope
plot_polytope(plot=fig,
polytope=poly_dt1000,
center=robot_position,
face_color='lightsalmon',
edge_color='orangered',
vertex_color='gray',
label='polytope 1s')
plot_polytope(plot=fig,
polytope=poly_dt500,
center=robot_position,
face_color='green',
edge_color='green',
vertex_color='green',
label='polytope 0.5s')
plt.grid()
plt.axis('equal')
plt.legend()
plt.show()