Mujoco examples

This is an example tutorial of how to setup mujoco with pycapacity to calculate and visualise the robot capacities and visualise it in the builtin mujoco visualiser.
Installing Mujoco
Mujoco library can be downloaded as sa pip package, however we suggest you to use anaconda to isolate the mujoco environment.
Pip package install
Install the mujoco library
pip install mujoco
Install an additional library with robot data robot_descriptions provided by mujoco community as well more info
pip install robot_descriptions
Finally install pycapacity for the workspace analysis
pip install pycapacity
Also you can install ipython of jupyter for simplicity.
Anaconda install
For anaconda instals you can simply download the yaml file and save it as env.yaml:
name: mj_examples
channels:
- defaults
- conda-forge
dependencies:
- python=3
- pip
- pip:
- pycapacity
- mujoco
- robot_descriptions
And create a new ready to go environment:
conda env create -f env.yaml # create the new environemnt and install pinocchio, gepetto, pycapacity,..
conda actvavte mj_examples
Visualise polytopes in Meshcat
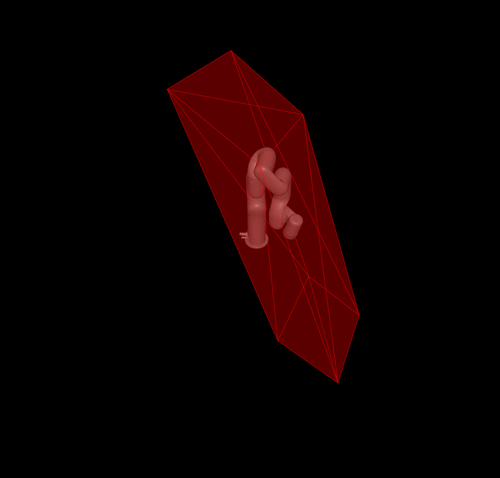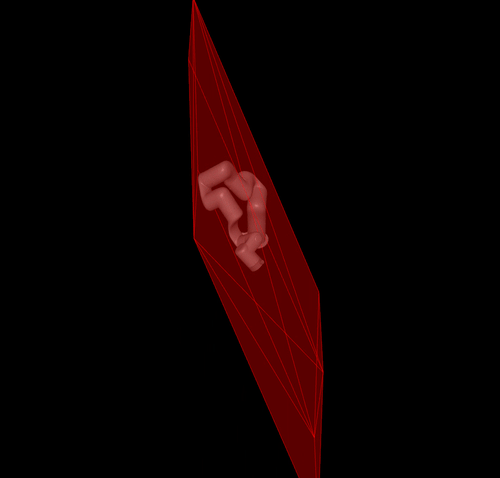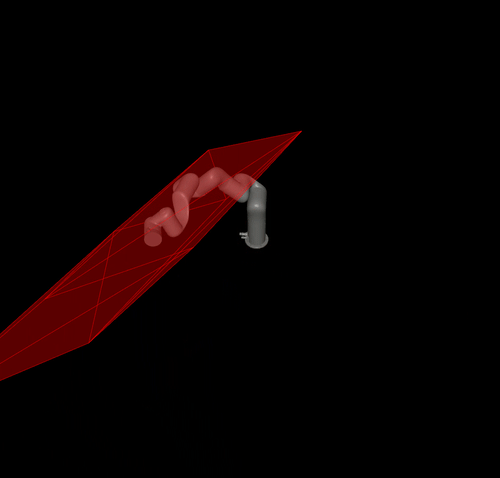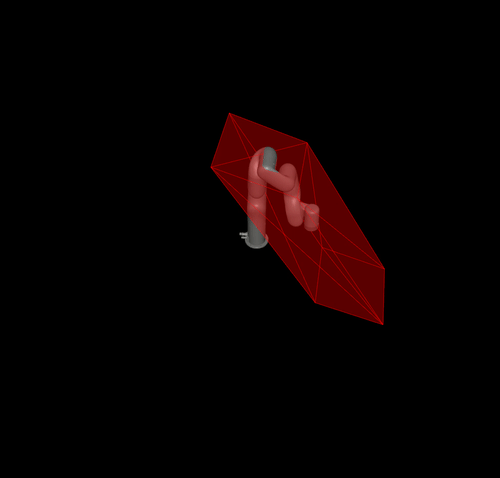
Calculating the velocity polytope and ellipsoid of the panda robot and visualising it using meshcat.
import mujoco
import mujoco.viewer
import numpy as np
from robot_descriptions.loaders.mujoco import load_robot_description
# Loading a variant of the model, e.g. panda without a gripper.
# model = load_robot_description("xarm7_mj_description", variant="xarm7_nohand"); frame_name = "link7"
# model = load_robot_description("iiwa14_mj_description"); frame_name = "link7"
# model = load_robot_description("gen3_mj_description"); frame_name = "forearm_link"
model = load_robot_description("panda_mj_description", variant="panda_nohand"); frame_name = "link7"
# model = load_robot_description("ur10e_mj_description"); frame_name = "wrist_3_link"
# model = load_robot_description("ur5e_mj_description"); frame_name = "wrist_3_link"
# model = load_robot_description("fr3_mj_description"); frame_name = "fr3_link6"
# Create a data structure to hold the state of the robot
data = mujoco.MjData(model)
# force polytope calculation function
from pycapacity.robot import force_polytope
# visualisation utils from pycapacity package
import pycapacity.visual as pyviz
# get max and min joint torques
tau_max = model.actuator_forcerange[:,1]
if np.any(tau_max <= 0):
print("Warning: Negative or zero torque limits detected, using default value of 10 Nm")
tau_max = np.ones_like(tau_max)*10
tau_min = -tau_max
# Launch viewer
with mujoco.viewer.launch_passive(model, data) as viewer:
while viewer.is_running():
mujoco.mj_step(model, data)
viewer.opt.flags[mujoco.mjtVisFlag.mjVIS_TEXTURE] = 0 # Disable textures
# Compute the Jacobian of the end-effector
J_pos = np.zeros((3, model.nv)) # Linear Jacobian (3xnq)
J_rot = np.zeros((3, model.nv)) # Rotational Jacobian (3xnq)
mujoco.mj_jacBodyCom(model, data, J_pos, J_rot, model.body(frame_name).id)
J = J_pos # Use only the linear Jacobian
# Compute the force polytope
poly = force_polytope(J, tau_min, tau_max)
# Shift polytope to the current end-effector position
# and scale it for easier visualization
poly.vertices = poly.vertices / 500 + data.site_xpos[0][:,None]
# Draw force polytope
pyviz.mj_draw_polytope(viewer, poly, edges=True, faces=True)
# Update the viewer
viewer.sync()

If you comment the panda robot import and uncomment the xaarm7 robot import
model = load_robot_description("xarm7_mj_description", variant="xarm7_nohand"); frame_name = "link7"
....
# model = load_robot_description("panda_mj_description", variant="panda_nohand"); frame_name = "link7"
you will get the following result:

Reachable worksapce approximation
Calculating the reachable workspace of the panda robot and visualising it using mujoco
import mujoco
import mujoco.viewer
import numpy as np
from robot_descriptions.loaders.mujoco import load_robot_description
# Loading a variant of the model, e.g. panda without a gripper.
model = load_robot_description("panda_mj_description", variant="panda_nohand"); frame_name = "link7"
# Set the timestep to 10ms
model.opt.timestep = 0.01
# Create a data structure to hold the state of the robot
data = mujoco.MjData(model)
# force polytope calculation function
from pycapacity.robot import reachable_space_nonlinear
# visualisation utils from pycapacity package
import pycapacity.visual as pyviz
# get max and min joint torques
q_max = model.actuator_ctrlrange[:,1]
q_min = model.actuator_ctrlrange[:,0]
# velocity limits from here: https://frankaemika.github.io/docs/control_parameters
dq_max = np.array([2.1750, 2.1750,2.1750,2.1750,2.6100, 2.6100,2.6100])
dq_min = -dq_max
# Create a data structure to hold the state of the robot (only for the FK calculation)
data1 = mujoco.MjData(model)
# A simple forward kinematics (FK) function
def fk(q):
data1.qpos[:7] = q
mujoco.mj_kinematics(model, data1)
return data1.site_xpos[0]
# Launch viewer
with mujoco.viewer.launch_passive(model, data) as viewer:
while viewer.is_running():
mujoco.mj_step(model, data)
viewer.opt.flags[mujoco.mjtVisFlag.mjVIS_TEXTURE] = 0 # Disable textures
# Compute the reachable space of the end-effector
poly = reachable_space_nonlinear(
forward_func= fk,
q0 = data.qpos[:7],
time_horizon= 0.2,
q_min=q_min,
q_max=q_max,
dq_min=dq_min,
dq_max=dq_max,
options= {'calculate_faces':True, 'convex_hull': False, 'n_samples': 3, 'facet_dim': 1}
)
# Draw force polytope
pyviz.mj_draw_polytope(viewer, poly, edges=True, faces=True)
# Update the viewer
viewer.sync()
📢 NEW Examples!
- For some more examples check out the
examplesfolder of the repository. Python scripts are available in the
examples/scriptsfolder: see on Github